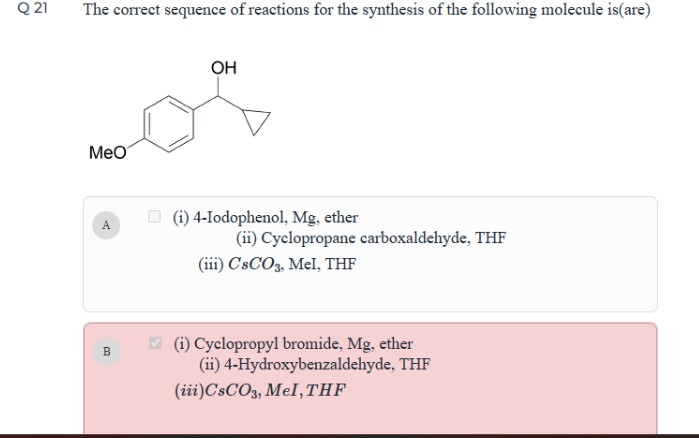
Organic Chem: Use of CsCO3
What is the use of CsCO3/MeI in this question? Also, can someone explain briefly where B and D go wrong?

8 Replies
@Dexter
Note for OP
+solved @user1 @user2... to close the thread when your doubt is solved. Mention the users who helped you solve the doubt. This will be added to their stats.Reduction iirc. Wait, I have this reaction.
Nevermind I was thinking of CdCO3
Oh, I think I got it. CsCO3 is probably acting like a base here (Cs is the most electropositive element) and abstracting the phenol acidic proton. Also breaking apart methyl iodide to give methyl carbocation.
$CsCO{3} + 2MeI \to CsI{2} + 2Me^{+} + CO{3}^{2-}$
$CO{3}^{2-}+2PhOH \to 2PhO^{-} + H{2}O + CO{2}$
Opt

Ah, I see. (It generates R+ and takes away H+)
Can you explain where B and D go wrong?
B goes wrong because phenol has an acidic proton. The carbanion never attacks the aldehyde because it gains H(+) from the phenol.
As for D, since it's an ester, the alkoxide leaves when the carbanion attacks, leaving behind a ketone. You'd need to reduce it to an alcohol afterwards, but the reagent is missing.
I see. Noice.
Thanks a lot man.
+solved @Opt
Post locked and archived successfully!
Archived by
<@1075951732460376214> (1075951732460376214)
Time
<t:1743075944:R>
Solved by
<@763645886500175892> (763645886500175892)