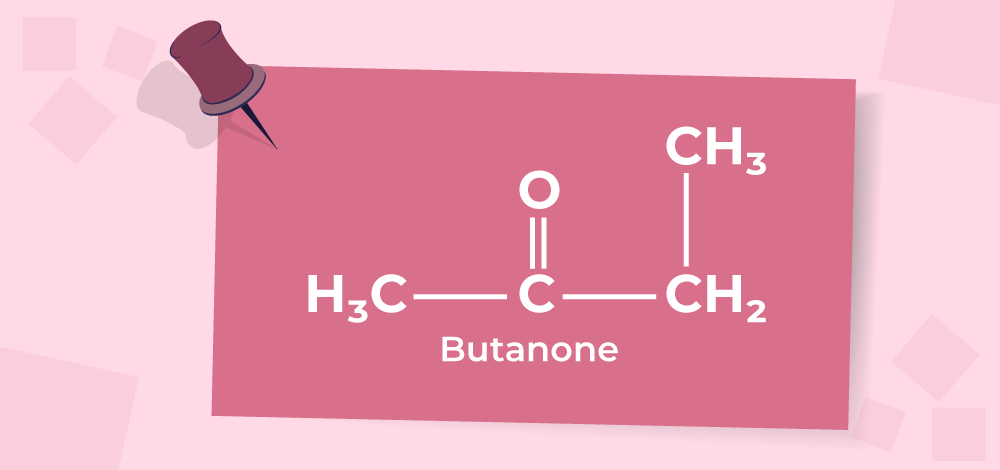
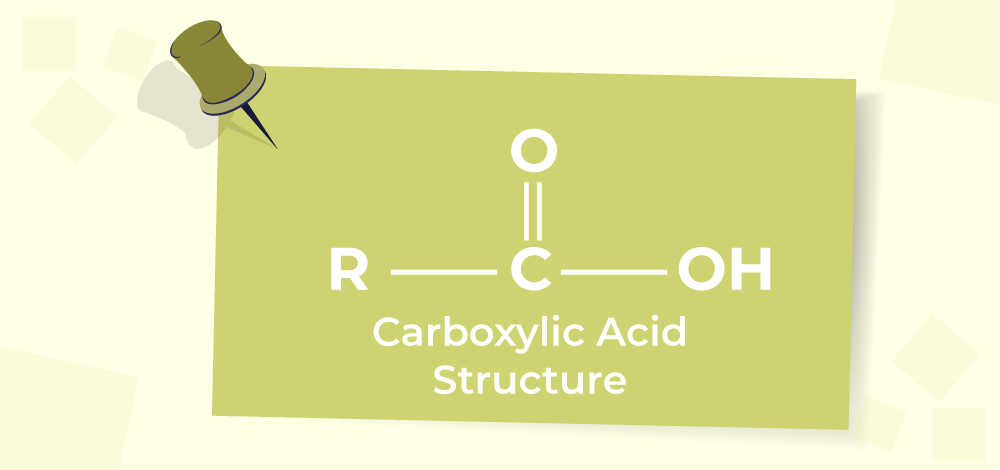
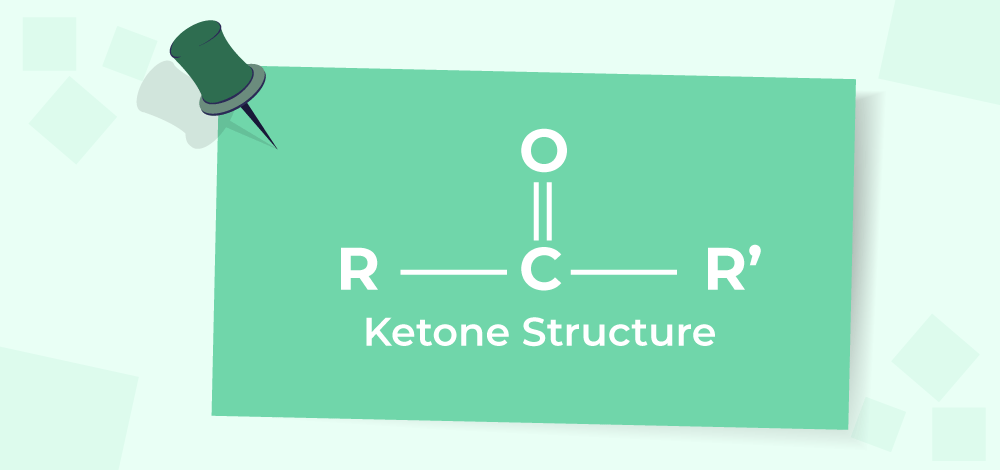
aldehydes ketones, theory doubt
what happens when we put strong oxidizing agent in excess on a secondary alcohol, i know the product but how do we get there and how does it happen
14 Replies
@Dexter
Note for OP
+solved @user1 @user2... to close the thread when your doubt is solved. Mention the users who helped you solve the doubt. This will be added to their stats.James Ashenhurst
Master Organic Chemistry
Alcohol Oxidation: "Strong" and "Weak" Oxidants
Overview of alcohol oxidation: what bonds form and break, and the key difference between PCC, Swern, and DMP versus H2CrO4, CrO3/H3O+ & KMnO4.
Does this help?
i think here its not in excess? the product i have is co2 + h2o
Ketones are generally resistant to mild oxidation, but under strong oxidative conditions, the C–C bond adjacent to the carbonyl can break.
• This cleavage is called oxidative cleavage, and it happens via hydration of the ketone followed by bond breaking.
Possible outcomes depend on the structure of the ketone:
• If the ketone has no hydrogen on the alpha carbon, oxidation leads to carboxylic acids.
• If further oxidation occurs, it can go all the way to carbon dioxide and water.
Here is chat gpt :p
This is an interesting way to show mechanisms



mechanisms till the enolate step^
post that the ene becomes OH too cos of MnO4-
then C-C bond breaks to form two moles of RCOOH or R1COOH + R2COOH (if R1, R2 are diff)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/oxidation-of-aldehydes-ketones-carboxylic-acids/
Last step is a redox rxn
GeeksforGeeks
Oxidation of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - GeeksforGeeks
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.


,rotate


+solved @iTeachChem
Post locked and archived successfully!
Archived by
<@852788017243357194> (852788017243357194)
Time
<t:1742397819:R>
Solved by
<@1035556259417571408> (1035556259417571408)